Showing 1612–1620 of 1965 results
-
Prepare general journal entries to record these transactions
$5.00Business transactions completed by Hannah Venedict during the month of September are as follows.
a. Venedict invested $84,000 cash along with office equipment valued at $23,000 in exchange for common stock of a new company named HV Consulting. b. The company purchased land valued at $35,000 and a building valued at $170,000. The purchase is paid with $35,000 cash and a long-term note payable for $170,000. c. The company purchased $1,700 of office supplies on credit. d. Venedict invested her personal automobile in the company in exchange for more common stock. The automobile has a value of $16,200 and is to be used exclusively in the business. e. The company purchased $5,400 of additional office equipment on credit. f. The company paid $1,900 cash salary to an assistant. g. The company provided services to a client and collected $7,000 cash. h. The company paid $645 cash for this month’s utilities. i. The company paid $1,700 cash to settle the account payable created in transaction c. j. The company purchased $20,300 of new office equipment by paying $20,300 cash. k. The company completed $6,750 of services for a client, who must pay within 30 days. l. The company paid $1,800 cash salary to an assistant. m. The company received $4,000 cash in partial payment on the receivable created in transaction k. n. The company paid $2,600 cash in dividends. Required: 1. Prepare general journal entries to record these transactions -
Total cost allocated to Accounting services using Activity-Based costing ABC
$2.00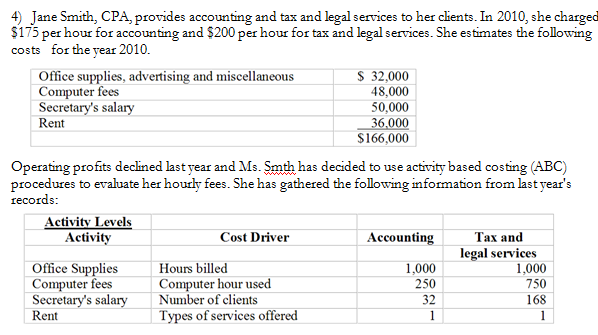
(a) What is the total cost allocated to Accounting services using Activity-Based costing ABC?
Text: 4) Jane Smith, CPA, provides accounting and tax and legal services to her clients. In 2010, she charged $175 per hour for accounting and $200 per hour for tax and legal services. She estimates the following Operating profits declined last year and Ms. Smits has decided to use activity based costing (ABC) procedures to evaluate her hourly fees. She has gathered the following information from last year’s records:
-
E3-16 Determining Accounting Equation Effects of Several Transactions [LO 3-2, LO 3-3]
$5.00In January 2013, Tongo, Inc., a branding consultant, had the following transactions. Indicate the accounts, amounts, and direction of the effects on the accounting equation under the accrual basis. A sample is provided. (Enter all amounts as positive values.) a. (Sample) Received $9,700 cash for consulting services rendered in January. b. Issued stock to investors for $11,500 cash. c. Purchased $21,500 of equipment, paying 25 percent in cash and owing the rest on a note due in 2 years. d. Received $8,450 cash for consulting services to be performed in February. e. Bought $1,250 of supplies on account. f. Received utility bill for January for $2,170, due February 15. g. Consulted for customers in January for fees totaling $16,300, due in February. h. Received $16,700 cash for consulting services rendered in December. i. Paid $625 toward supplies purchased in (e). -
The Mitsui Travel E-Marketing Plan
$49.00The Mitsui Travel E-Marketing Plan
E-Marketing Plan Instructioms
Please see below what you need to do in brief for the e-marketing plan – [as per the rubric attached in Blackboard]
- Introduction: Focus on the company (first paragraph) and its industry (second paragraph).
- Situation Analysis and SWOT analysis: Focus on the micro and macro environmental factors that the company is facing with special reference to the company’s online presence. Then you need to prepare a SWOT table for the company – list of S (Strength of the company), W (Weaknesses), O (Opportunities) and T (Threats).
- E-Marketing strategic planning: Focus on company’s segmentation, targeting, differentiation and positioning strategies especially for its operations in online. i.e. what specific customer base the company is targeting by going online, how it is differentiating from its competitors, and how it is positioning its offers to the customers’ mind.
- E-marketing objectives: State 2 to 3 e-marketing objectives that the company may wish to achieve in next 1-2 years. It could be increasing online customer base by XX%, as an example.
- Marketing mix strategies – Now you need to recommend 4 P strategies through which the company can achieve the above mentioned objectives and describe those strategies.
- Implementation – In order to implement the planned strategies, you need to execute several relevant activities such as – making the website more interactive (as an example), pursuing AdWords PPC campaign, something like that… Thus, in this section, you need to discuss the relevant activities that are required to execute in order to implement the 4 P strategies.
- Budget and Evaluation – This is more of arbitrary than actual numbe
- You need to guess realistically how much the company need to spend for all these activities. Then discuss how you will measure/evaluate the effectiveness of your plan i.e. specifically what matrix you will look for to check whether you have achieved your objectives or not.
12 pages
14 References
-
Assume a bank loan requires an interest payment of $85 per year…
$1.00Assume a bank loan requires an interest payment of $85 per year and a principal payment of $1,000 at the end of the loan’s eight-year life.
a. At what amount could this loan be sold for to another bank if loans of similar quality carried an 8.5 percent interest rate? That is, what would be the present value (PV) of this loan?
b. Now, if interest rates on other similar quality loans are 10 percent, what would be the PV of this loan?
c. What would be the PV of the loan if the interest rate is 8 percent on similar quality loans?
-
Analysis of Accounting events
$5.00Analyze the events listed below by indicating the accounts and amounts involved in the table below. In the column labeled “+/-“, select the sign that describes how the category is affected. If the event should not to be recorded as a transaction, leave it blank. A. Borrowed $760,000 cash, signing a promissory note. B. Bought a factory for $920,000, paying $230,000 in cash and signing a promissory note for $690,000. C. Rented equipment and issued a check for 6 months at $16,000 a month. D. Provided $135,000 of services and billed customers. E. Purchased $42,000 of supplies on account. F. Received a utility bill for the current period in the amount of $2,400. G. Raised sales prices on 200 units from $420 per unit to $500 per unit. H. Received a 50% deposit from a customer on a $32,000 order to be filled next month. -
Prepare general journal entries
$3.00a. To launch the company, Jenna Aracel, the owner, invested $250,000 cash, office equipment with a value of $9,800, and $70,000 of drafting equipment in exchange for common stock. b. The company purchased land worth $54,000 for an office by paying $8,800 cash and signing a long-term note payable for $45,200. c. The company purchased a portable building with $56,000 cash and moved it onto the land acquired in b. d. The company paid $4,000 cash for the premium on an 18-month insurance policy. e. The company completed and delivered a set of plans for a client and collected $6,100 cash. f. The company purchased $32,000 of additional drafting equipment by paying $11,000 cash and signing a long-term note payable for $21,000. g. The company completed $16,000 of engineering services for a client. This amount is to be received in 30 days. h. The company purchased $1,850 of additional office equipment on credit. i. The company completed engineering services for $24,000 on credit. j. The company received a bill for rent of equipment that was used on a recently completed job. The $1,445 rent cost must be paid within 30 days. k. The company collected $8,000 cash in partial payment from the client described in transaction g. l. The company paid $1,500 cash for wages to a drafting assistant. m. The company paid $1,850 cash to settle the account payable created in transaction h. n. The company paid $1,045 cash for minor maintenance of its drafting equipment. o. The company paid $9,500 cash in dividends. p. The company paid $2,200 cash for wages to a drafting assistant. q. The company paid $3,600 cash for advertisements on the Web during June. Required: 1. Prepare general journal entries to record these transactions. -
Tackling the free rider problem
$10.00Tackling the free rider problem
How might the free rider problem be tackled differently in the cases of:
A) paying for Australia’s national defense?
B) paying for public transport in any of the capital cities?
-
Post each transaction to the T accounts
$3.00Transactions
May 1 Terry purchased computer equipment for $8,400, paying $1,000 now, and issuing a promissory note for the balance; the note is due in monthly installments of $500 plus interest at 10% on the unpaid balance.
8 Terry records service revenue earned: $3,200 from cash customers; $12,000 for customers billed for completed services.
22 Common stock is issued for land with a fair value of $35,000.
31 An invoice for $1,200 is received from the company’s advertising agency for ads which were run on radio and TV during May; the invoice is due in 30 days.
Refer to the transactions for Terry Company.
Use the transactions incurred by the Terry Corporation to set up T accounts and post each transaction to the T accounts.